The Sigatoka disease of banana is also known as leaf spot disease of banana, this are two types of disease which are Yellow sigatoka disease and Black sigatoka disease of banana.
The Sigatoka disease of banana was first reported in Java in 1902 and later in 1913, it appears in epidemic form in Sigatoka Valley in Fiji.
Besides India occurrence of the disease has been reported in many banana-growing countries like Columbia, Mexico, Uganda, and Venezuela.
In India, It is a major problem in the growing states like Andhra Pradesh, Assam, Bihar, Gujarat, Karnataka, Kerala Maharashtra, Tamilnadu, and West Bengal.
Taxonomy Classification of Sigatoka disease:
| Kingdom | Fungi |
| Division | Ascomycota |
| Class | Dothideomycetes |
| Order | Capnodiales |
| Family | Mycosphaerellaceae |
| Genus | Cercospora |
| Species | C.musae.zimm |
Causal Organism(Pathogen):
The Sigatoka disease of Banana is caused by the fungus Cercospora musae Zimm. The perfect stage of the fungus is Mycospharella musicola Leach.
The Yellow Sigatoka disease of banana is caused by Mycosphaerella musicola and Black sigatoka disease of banana is caused by Mycosphaerella fijiensis.
Conidia are elongated, narrow, and multi-septate and 20-30 *2-6 micron meters in size. Perithecia are dark brown to black and asci are oblong, clavate, and measure 28.8-36.8 * 8.0-10.8 micrometers. Ascospores are single separate, hyaline, obtuse with an upper cell that is slightly broader.
Survival and Spread:
The conidia of the fungus are carried by old dried infected leaves, wind, and rain water and they help to spread the disease.
Favorable conditions:
- The most favorable condition of Sigatoka disease of Banana is high humidity, rainy weather, and heavy frost with temperature ranging from 20-30 degree Celsius.
- The disease is more severe in moist conditions as surface moisture is required for the spreading of the disease.
- Poor drainage system and less fertility of soils.
- Unbalanced utilization of potassium fertilizer.
Symptoms:
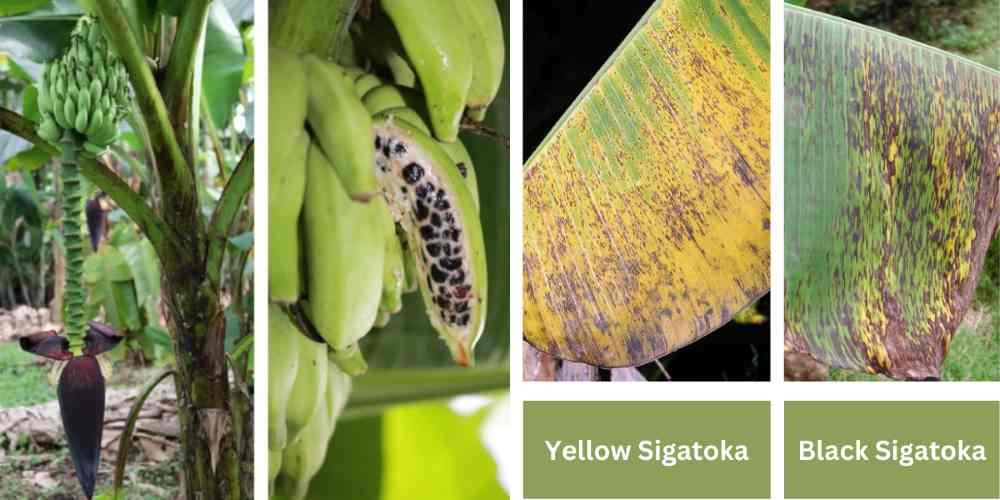

- The initial symptoms of the Sigatoka disease of banana appear on the young leaves i.e, a third or fourth leaf from the top.
- Spindle-shaped spots with greyish centers which are surrounded by a yellow halo are developed in the leaf lamina and later convert into brownish-green narrow streaks.
- The streaks enlarge in size and become linear-oblong brown to black spots with dark brown brands and a yellow halo.
- Black speaks of fungal fructification appearing in the affected leaves. Due to the development of numerous spots, rapid drying of leaves takes place and the dried leaves remain hanging on the pseudostem.
- At the time of heavy infection, if banana fruits attain maturity, individual bananas remain undersized, ripen unevenly and their flesh develops a buff pinkish color. These bananas can’t be stored for a longer period.
Symptoms of Yellow Sigatoka Disease
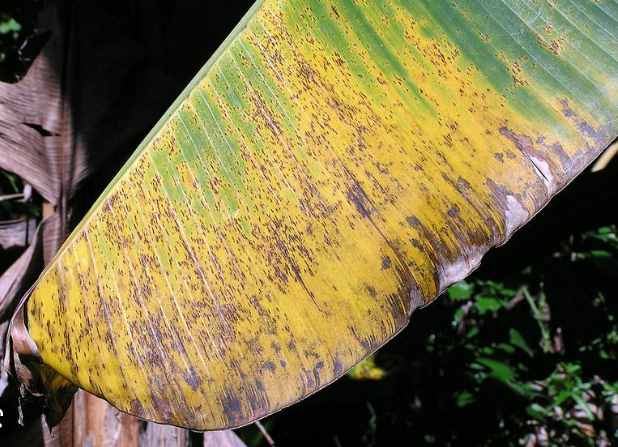

- Symptoms start as minute yellow, green aspect 1mm long that grow into long yellow streaks.
- Later the extreme broader and form a large spot with a sunken center, yellow halo, and dark brown margin.
- The leaf tissue dried rapidly and the large area of the leaves turn into brown and grey color.
Symptoms of Black Sigatoka disease
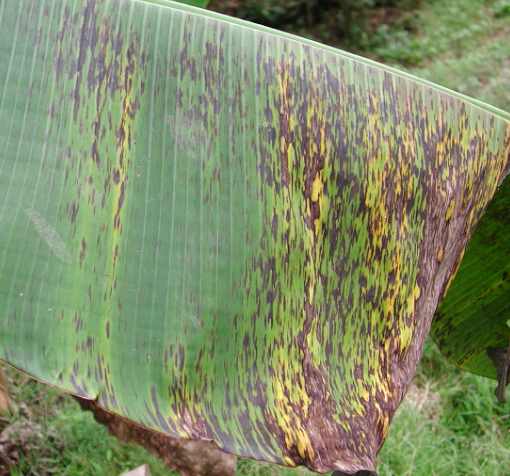

- Symptoms are similar to the yellow Sigatoka aspect in that the streaks are rusty reddish to brown which later become black and found the characteristic black streaks of the leaf.
- Heavily spotted leaves look black hence the name black Sigatoka.
- The spot-reduced photosynthesis results in yield loss, and the fruit ripens pre-maturity in the fields and during transit which makes them unmarketable. If you want to read more details about Black sigatoka disease.
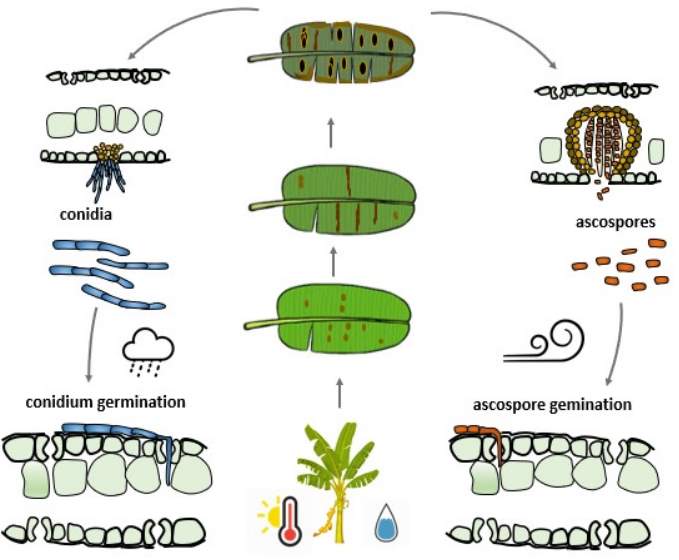
Sigatoka disease of banana Disease Cycle:
The pathogen survives on dry infected leaves lying on soils and the primary infection takes place through ascospores produced in the infected plant debris.
The secondary infections take place by conidia disseminated through winds and rainwater.
The disease is favored by the temperature ranging from 23 – 25 degree Celsius, high humidity within the plantation due to rain, poor drainage, closer spacing, heavy weed infestation, frequent irrigation, and more numbers of suckers per mat.
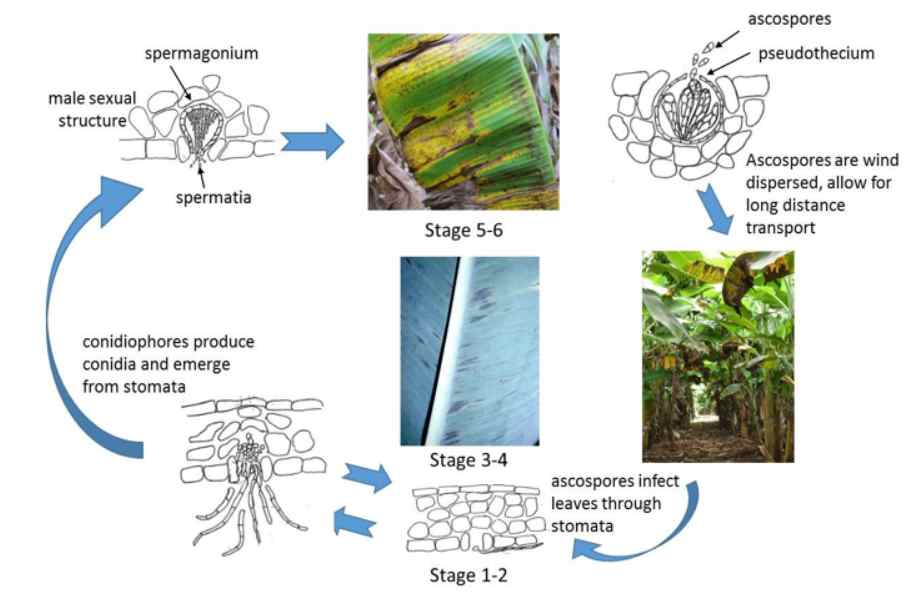
Spores are formed on the upper leaf surface in the dead, grey patches. They are released during showers or periods of high humidity and are blown on the undersides of growing leaves by wind and rain, and the cycle begins again.
Conidia are assumed to be responsible for short-distance dissemination within the plantation, whilst ascospores are thought to be responsible for longer-distance spread. Infected planting material might potentially spread the virus. There is also evidence that tainted fruit exports might transmit the disease, particularly if dead plant material is present.
Management and control:
There are many ways to control of sigatoka disease of banana, which are described as given below:
- Water should not be allowed to accumulate around the plant and periodical weeding should be done.
- Selection of well-drained soils and growing disease-resistant varieties.
- Keep the banana field as weed free and remove the suckers timely.
- Avoid planting at close spacing, plants are planted at the recommended spacing about 2.5 m apart; this is about 1600 plants to the ha.
- Avoid excessive use of potassium fertilizers.
- Removal of excess sucker from the banana mat is important to facilitate air circulation and thereby reduce the humidity within the plantation.
- Removal and destruction of affected leaves followed by spraying with Bordeaux Mixture 1%+line sheet oil 0.3%.
- Spraying of Carbendazim 50 WP 0.05% and Mineral oil at the rate 0.3% or Mancozeb 75 WP 0.2% along with sticker/spreader-like triton at the rate 1 ml/lit.
FAQs
Which fungicide is useful for Sigatoka disease in banana?
The following fungicides are mostly used in management of Sigatoka disease of banana, Spraying of Carbendazim 50 WP 0.05% and Mineral oil at the rate 0.3% or Mancozeb 75 WP 0.2% along with sticker/spreader-like triton at the rate 1 ml/lit.
Sigatoka disease in banana caused by
The Sigatoka disease of Banana is caused by the fungus Cercospora musae Zimm. The perfect stage of the fungus is Mycospharella musicola Leach.
Yellow sigatoka disease in banana caused by
The Yellow Sigatoka disease of Banana is caused by the fungus Mycosphaerella musicola.
Black sigatoka diseases of banana caused by
The Black Sigatoka disease of Banana is caused by the fungus Mycosphaerella fijiensis.
What are the taxonomy classification of sigatoka disease?
Kingdom: Fungi, Division: Ascomycota, Class: Dothideomycetes, Order: Capnodiales, Family: Mycosphaerellaceae, Genus: Cercospora , Species: C.musae
Sigatoka disease of banana is transmitted by
The Sigatoka disease of banana is transmitted by old dried infected leaves, wind, and rain water and they help to spread the disease.
The Sigatoka disease of banana was first reported in ?
The Sigatoka disease of banana was first reported in Java in 1902 and later in 1913, it appears in epidemic form in Sigatoka Valley in Fiji.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Sigatoka disease of banana is very harmful to banana production. If you face these problems in your banana cultivation areas, follow the above-mentioned controls and management methods to help prevent your losses from these diseases. If you have any questions related to this Disease leave a comment below.
In case you missed it:
Objectives Of Plant Breeding-Definition-History And Scope
Basic Principles Of Agronomy, Importance, And Scope
